© All rights reserved galwayclinic.com 2013

In most cases there is an
extra electrical circuit in the
heart.
This allows the hearts electrical impulse to go from the top to the bottom of the heart and then turn around and go back from the bottom to the top of the heart. Normally the impulse can only go from the top to the bottom of the heart. Following this a new heartbeat starts at the top of the heart (from the hearts own pacemaker or sinus node) and travel through a junction in the middle of the heart (AV node) and continue to the hearts two lower chambers. Following an electrical impulse which takes milliseconds, the heart muscle responds and pumps blood (a heartbeat).Sometimes there is an extra
electrical circuit in the
middle of the heart (AV node)
This allows an impulse to spread from the middle of the heart to the upper and lower chambers simultaneously. This is the most common type of regular rapid heart rate that we see. On the other hand, some arrhythmias are common, so-called benign arrhythmias, and aren't associated with health problems. These often require investigation with an ultrasound of the heart (echocardiogram) to make sure that the heart muscle and valves are working normally.In the past, the only
treatments for abnormally
fast heart rhythms, known as
tachycardias, was
medication or, in extreme
cases, open heart surgery.
Today, radiofrequency catheter ablation is widely used to cauterise the abnormal electrical pathway that causes the condition. The procedure delivers a pinpoint of heat inside the heart. Another procedure, called cryoablation, destroys the abnormal cells or electrical pathway by freezing.Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm created by a disturbance in the heart's electrical system. During an arrhythmia, the heart may beat too fast, too slow or in an irregular pattern. In most arrhythmias the heart beats rapidly for seconds, minutes or rarely hours at a time
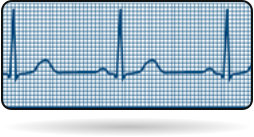
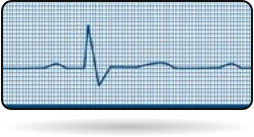
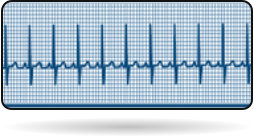

Normal Heart beat (50 - 100)
Bradycardia (<60 beats per min)
Tachycardia (>100 beats per min)
Galway Clinic Facebook page
Tel: +353 (0) 91720170 brendan.ocochlain@galwayclinic.com


Galway Site Design

In most cases there is an extra electrical
circuit in the heart.
This allows the hearts electrical impulse to go from the top to the bottom of the heart and then turn around and go back from the bottom to the top of the heart. Normally the impulse can only go from the top to the bottom of the heart. Following this a new heartbeat starts at the top of the heart (from the hearts own pacemaker or sinus node) and travel through a junction in the middle of the heart (AV node) and continue to the hearts two lower chambers. Following an electrical impulse which takes milliseconds, the heart muscle responds and pumps blood (a heartbeat).Sometimes there is an extra electrical circuit
in the middle of the heart (AV node)
This allows an impulse to spread from the middle of the heart to the upper and lower chambers simultaneously. This is the most common type of regular rapid heart rate that we see. On the other hand, some arrhythmias are common, so-called benign arrhythmias, and aren't associated with health problems. These often require investigation with an ultrasound of the heart (echocardiogram) to make sure that the heart muscle and valves are working normally.In the past, the only treatments for abnormally
fast heart rhythms, known as tachycardias,
was medication or, in extreme cases, open
heart surgery.
Today, radiofrequency catheter ablation is widely used to cauterise the abnormal electrical pathway that causes the condition. The procedure delivers a pinpoint of heat inside the heart. Another procedure, called cryoablation, destroys the abnormal cells or electrical pathway by freezing.Arrhythmias
An arrhythmia is an abnormal heart rhythm created by a disturbance in the heart's electrical system. During an arrhythmia, the heart may beat too fast, too slow or in an irregular pattern. In most arrhythmias the heart beats rapidly for seconds, minutes or rarely hours at a time
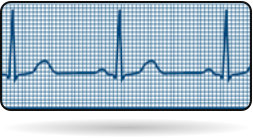
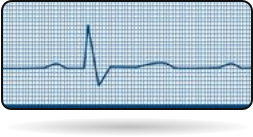
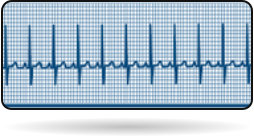

Normal Heart beat (50 - 100)
Bradycardia (<60 beats per min)
Tachycardia (>100 beats per min)

Galway Clinic Facebook page