© All rights reserved galwayclinic.com 2013

Galway Clinic Facebook page
Tel: +353 (0) 91720170 brendan.ocochlain@galwayclinic.com
Biventricular pacemaker
What is cardiac resynchronization therapy?
• Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is used to treat the delay in heart ventricle contractions that occur in some people with advanced heart failure • Heart failure means the heart’s pumping power is weaker than normal. With heart failure, blood moves through the heart and body at a slower rate, and pressure in the heart increases. A delay between the contraction of the right and left ventricles often occurs with heart failure, so the walls of the left ventricle are unable to contract at the same time. • The CRT pacing device (also called a biventricular pacemaker) is an electronic, battery-powered device that is surgically implanted under the skin. • The device has 2 or 3 leads (wires) that are positioned in the heart to help the heart beat in a more balanced way. The leads are implanted through a vein in the right atrium and right ventricle and into the coronary sinus vein to pace the left ventricle.How it works:
In some patients with heart failure the electrical impulses travel slowly through the heart leading to inefficient contraction and leaking of the mitral valve. This results in shortness of breath on exertion and worsening heart failure. These patients have a condition called left bundle branch block. The biventricular pacemaker corrects the condition as there are pacemaker leads to pace the upper chambers and two lower chambers in a normal organised fashion. In patients with a dilated weakened heart (dilated cardiomyopathy), the pacemaker can lead to a significant improvement in exercise tolerance and reduced heart failure symptoms.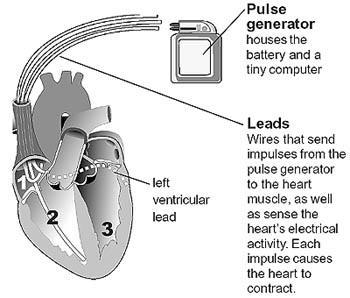
The CRT device (biventricular pacemaker) has 2 or 3
leads that are positioned in the:
1.
Right atrium
2.
Right ventricle
3.
Left ventricle (via the coronary sinus vein)

Galway Site Design


Galway Clinic Facebook page


Biventricular pacemaker
What is cardiac resynchronization therapy?
• Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is used to treat the delay in heart ventricle contractions that occur in some people with advanced heart failure • Heart failure means the heart’s pumping power is weaker than normal. With heart failure, blood moves through the heart and body at a slower rate, and pressure in the heart increases. A delay between the contraction of the right and left ventricles often occurs with heart failure, so the walls of the left ventricle are unable to contract at the same time. • The CRT pacing device (also called a biventricular pacemaker) is an electronic, battery-powered device that is surgically implanted under the skin. • The device has 2 or 3 leads (wires) that are positioned in the heart to help the heart beat in a more balanced way. The leads are implanted through a vein in the right atrium and right ventricle and into the coronary sinus vein to pace the left ventricle.How it works:
In some patients with heart failure the electrical impulses travel slowly through the heart leading to inefficient contraction and leaking of the mitral valve. This results in shortness of breath on exertion and worsening heart failure. These patients have a condition called left bundle branch block. The biventricular pacemaker corrects the condition as there are pacemaker leads to pace the upper chambers and two lower chambers in a normal organised fashion. In patients with a dilated weakened heart (dilated cardiomyopathy), the pacemaker can lead to a significant improvement in exercise tolerance and reduced heart failure symptoms.
The CRT device (biventricular pacemaker) has 2 or 3
leads that are positioned in the:
1.
Right atrium
2.
Right ventricle
3.
Left ventricle (via the coronary sinus vein)